If you think that the internet has changed your life, think again. The IoT is about to change it all over again!
What Is IoT?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of physical devices around the world connected to each other via the Internet. Collecting and sharing data. Connecting up all these different objects and adding sensors to them adds a level of intelligence to these devices, enabling them to communicate real-time data without involving a human being. These devices range from ordinary household objects like bulbs, thermostats to sophisticated industrial tools, computers, etc. Previously Bluetooth and RF (radio frequency) were used to control IoT applications, but they were limited to a short distance. Adding MQTT capabilities can help in overcoming inter-communication problems by securely automating IoT appliances.
What Is MQTT?
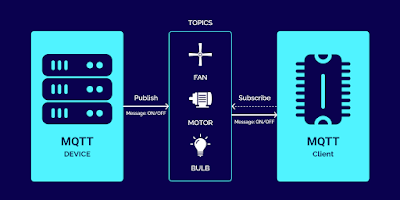
MQTT is one of the most commonly used protocols in IoT projects. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a messaging protocol that works on top of the TCP/IP protocol. MQTT can also run on SSL/TLS. SSL/TLS is a secure protocol built on TCP/IP to ensure that all data communication between devices is encrypted and secure. MQTT is a lightweight protocol that uses publish/subscribe operations to exchange data between clients and the server. Furthermore, its small size, low power usage, minimized data packets and ease of implementation make the protocol ideal for the “machine-to-machine” or “Internet of Things” world. Unlike HTTP’s request/response paradigm, MQTT is event-driven, and clients receive published messages. This type of architecture decouples the clients from each other to enable a highly scalable solution without dependencies between data producers and data consumers.
How does MQTT work?
MQTT uses your existing Internet home network to send messages to your IoT devices and respond to the messages.
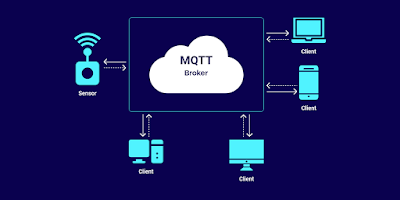
At the core of MQTT is the MQTT broker and the MQTT clients. The broker is responsible for dispatching messages between the sender and the rightful receivers. An MQTT client publishes a message to a broker and other clients can subscribe to the broker to receive messages. Each MQTT message includes a topic. A client publishes a message to a specific topic and MQTT clients subscribe to the topics they want to receive. The MQTT broker uses the topics and the subscriber list to dispatch messages to appropriate clients. If the connection from a subscribing client to a broker is broken, then the broker will buffer messages and push them out to the subscriber when it is back online. If the connection from the publishing client to the broker is disconnected without notice, then the broker can close the connection and send subscribers a cached message with instructions from the publisher.
MQTT Components:
In MQTT there are a few basic concepts that you need to understand:
Broker – The broker is the server that distributes the information to the interested clients connected to the server. This is the heart of the publish/subscribe protocol. The MQTT Broker is optimally designed to handle many thousands of concurrently connected MQTT clients.
Client – The device that connects to broker to send or receive information. The MQTT Client, be it Subscriber or Publisher (or both in one device) is any device from small Microcontroller up to a fully-fledged server, that has an MQTT library running and is connected to an MQTT Broker over any kind of network.
Topic – Messages make their way from a publisher, through a broker, to one or more subscribers using topics. Topics are hierarchical UTF-8 strings. Clients publish, subscribe, or do both to a topic. In other words, topics are the way you register interest for incoming messages or how you specify where you want to publish the message.
Publish – Clients that send information to the broker to distribute to interested clients based on the topic name.
Subscribe – Clients tell the broker which topic(s) they’re interested in. When a client subscribes to a topic, any message published to the broker is distributed to the subscribers of that topic. Clients can also unsubscribe to stop receiving messages from the broker about that topic.
QoS – Quality of Service. Each connection can specify a quality of service to the broker with an integer value ranging from 0-2. The QoS does not affect the handling of the TCP data transmissions, only between the MQTT clients.
1. specifies at most once, or once and only once without requiring an acknowledgment of delivery. This is often referred to as fire and forget.
2. specifies at least once. The message is sent multiple times until an acknowledgment is received, known otherwise as acknowledged delivery.
3. specifies exactly once. The sender and receiver clients use a two-level handshake to ensure only one copy of the message is received, known as assured delivery.
How to Use MQTT in Home Automation?
In today’s world, automation has become important and is being used in many applications in our daily life. A Home Automation System (HAS) is a system where in home appliances or environment is controlled without much human involvement. It saves power, time and efforts and is more efficient than the conventional systems. Home environmental monitoring is a major Internet of Things (IoT) application, which involves monitoring the inside and outside environment of the home. By using IoT technology, user can create advanced Home Automations Systems that can improve the quality of the life.
Let’s take one such example.
Example:
Let’s say our Home Automation System consists of an electric light bulb that can be controlled with the help of a mobile device. User will use mobile application to toggle light switch and this state will be sent to the mqtt broker. On the other side, electric light bulb with help of microcontroller receives the state sent by user. For this to happen, the mobile device will first define the topic it wants to publish on, then only it will publish the message. Meanwhile, the microcontroller attached to the light bulb subscribes to the same topic. Then once it receives the message that the device has published, it toggles light based on the state. It might also want to publish to another topic so that other clients can monitor the state of that light. Again, the broker role here is to take the message and deliver it to subscribed clients.
Topics are the way you register interest for incoming messages or how you specify where you want to publish the message. Topics are represented with strings separated by a forward slash. Each forward slash indicates a topic level. And also remember topics are case-sensitive. If you want to control multiple light across multiple rooms, you will need to come up with unique topic for these lights. Let’s suppose If we want to toggle bedroom light, the topic will be home/bedroom/lamp.
Now that we have 2 clients the first mobile application will publish to the topic “home/bedroom/lamp” with a message of “on” or “off” every time we push a button from app. In our demo we are using “MyMqtt” app from google play store. The second client will subscribe to “home/bedroom/lamp” and respond to the message by turning a light bulb on or off. And later it will publish with a message of “on” or “off” to another topic like “bedroom/lamp/state” so that other clients can monitor the state of that light.
Cloud for MQTT brokers?
MQTT on-premise broker is a rather time-consuming and demanding solution for any project. If we are talking about the quick launch of the solution for the Internet of things, then launching your own data center with a server for the MQTT broker will require resources for the initial launch and installation. Plus, expanding and scaling the on-premises broker creates a lot of problems when migrating to new servers.
Now let’s compare this solution with a cloud service, where for a minimal cost you can quickly connect your project to high-quality service and start using the MQTT protocol. With a cloud service, you also get support for your project and an already configured security system on the server and the ability to increase your capacities almost without limit. Placing the MQTT broker in the cloud can be a successful strategy both for small projects and for corporate-level projects.
Cloud-based MQTT brokers are many, like:
- Amazon
- Cloud MQTT
- Google Cloud IoT Core
- Heroku
- IBM
- Microsoft Azure IoT
Conclusion
MQTT is a communication protocol based on a publish and subscribe system. It is simple to use and it is great for Internet of Things and Home Automation projects. On the other hand, choosing a right cloud provider to service MQTT also gives you a lot of options now and you can use the message broker in your existing cloud, or choose the most suitable for your task.